Digital certificates
Introduction
Digital signatures are a way of validating the authenticity of digital documents and identifying the sender (signing with a digital signature indicates that the original message, document or file is safe and has not been tampered with).
As mentioned earlier on, there are four main purposes of digital signatures:
- authentication
- non-repudiation
- data integrity
- confidentiality
A digital signature is a digital code which is often derived from the digital certificate (described below), although other methods of generating digital signatures will be described throughout this section.
This also needs a lot of processing time to encrypt everything in the message.
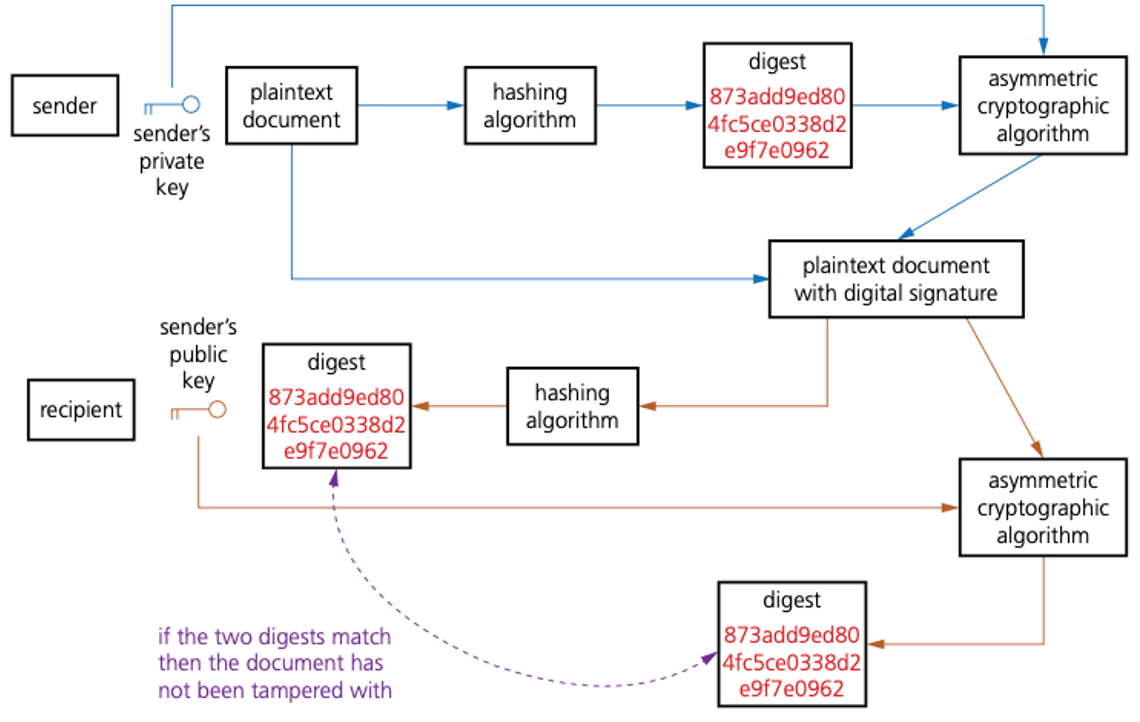
The following method, which is used to identify the sender and ensure the message was not tampered with, does not encrypt the messages but uses a generated numerical value known as a digest.
With this method, to actually identify the sender, it is not necessary to encrypt the whole message.
The plaintext message is put through a hashing algorithm which produces the digest.
For example, if the first page of this chapter was going to be sent, we could put it through a hashing algorithm (such as MD4) and it would produce a digest, for example, it might produce the following digest:
873add9ed804fc5ce0338d2e9f7e0962
However, this method still is not safe enough, since the public key could be forged by a third party, which means the recipient still cannot be certain that the message came from a legitimate source.
Therefore, an even more robust system is needed to give confidence that the sender is really who they claim to be.
A digital certificate is an electronic ‘document’ used to prove the online identity of a website or an individual.
The certificate contains a public key and other information identifying the owner of the certificate.
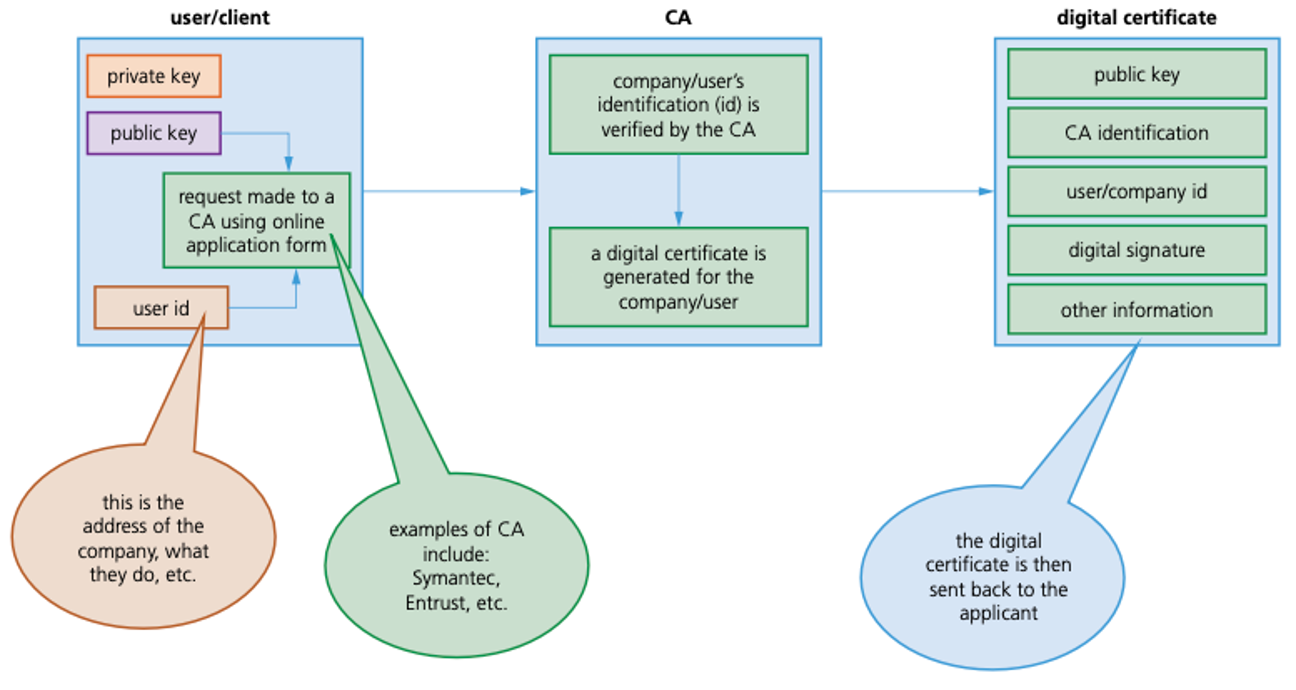
A digital certificate is issued by the certificate authority (CA) – they independently validate the identity of the certificate owner.
This is a list of the items commonly found on a digital certificate:
- version number
- serial number of certificate
- algorithm identification
- name of certificate issuer
- validity (start date and expiry date of certificate)
- company details
- public key
- issuer’s identifier
- company’s identifier
- signature algorithm used
- digital signature
How a user can apply for a digital certificate